Understanding the Basics of a Steel Fabrication Shop
What is a Steel Fabrication Shop?
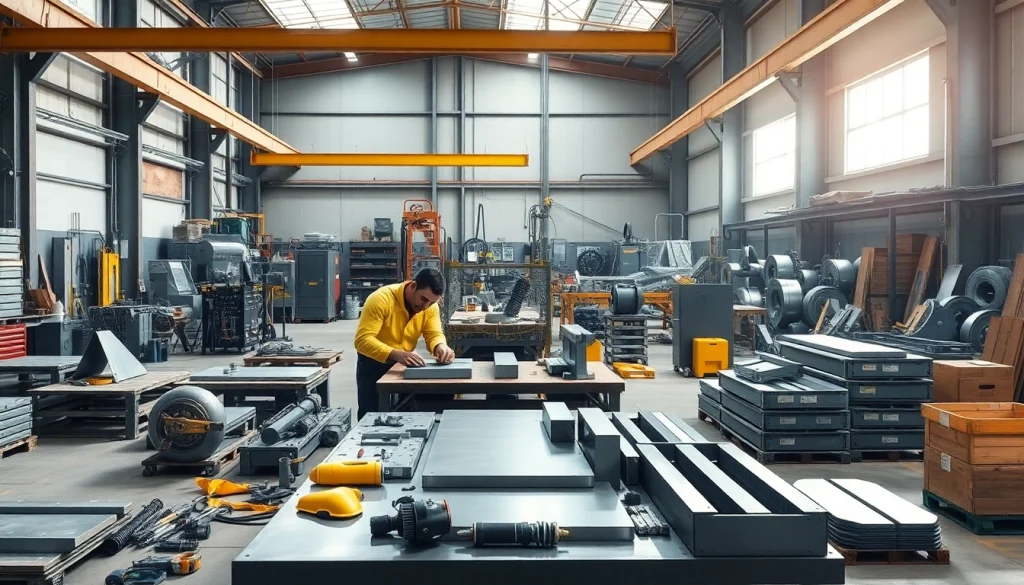
A steel fabrication shop is a specialized facility where steel and metal components are created, modified, and assembled into finished products. These shops play a crucial role across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. They are designed to transform raw steel materials into structurally sound components that meet specific engineering standards and client requirements.
At its core, the process of steel fabrication involves various operations, such as cutting, welding, bending, and assembling, which may vary in complexity and scope depending on the project at hand. Fabrication shops often cater to both large-scale industrial needs and smaller projects, reflecting the versatility and importance of steel in modern infrastructure and manufacturing.
Key Components of a Steel Fabrication Shop
In order to function effectively, a steel fabrication shop comprises several key components:
- Workforce: Skilled labor is essential. This includes engineers, fabricators, welders, and quality inspectors who ensure work quality and adherence to safety standards.
- Materials: The primary raw material is steel, which comes in various grades and forms such as sheets, plates, bars, and tubular shapes.
- Machinery: A variety of equipment is necessary, such as cutting machines, welding setups, bending equipment, and finishing tools.
- Workspace: A well-organized layout allows for the efficient movement of materials and personnel, facilitating a smooth workflow.
- Quality Control Systems: These systems ensure that all products meet industry standards and specifications before delivery.
Common Processes in Steel Fabrication
Several fundamental processes are integral to steel fabrication:
- Cutting: Steel components are initially cut to size using various methods like sawing, plasma cutting, or laser cutting.
- Bending: Steel sections are bent using press brakes or roll bending to achieve the desired angles and shapes.
- Welding: Joining pieces of steel together is done through various welding techniques, including MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
- Finishing: Surface treatments such as painting, powder-coating, or galvanizing are applied to enhance durability and aesthetics.
- Assembly: Final assembly involves putting together pre-fabricated components to form the end product, often verified by quality control personnel.
Essential Tools and Equipment in Steel Fabrication Shop
Machinery and Tools Overview
The array of machinery and tools utilized in a steel fabrication shop is numerous and diverse, each serving unique purposes. Key equipment includes:
- Plasma Cutters: Used for high-precision cutting of steel sheets and plates.
- Welding Machines: Essential for joining metal parts, available in several configurations such as MIG and TIG welders.
- Press Brakes: Machines that bend metal to specific angles, crucial for forming structural components.
- Band Saws: Employed for cutting metal at various thicknesses with precision.
Safety Equipment in Steel Fabrication
Ensuring the safety of all workers is paramount in a steel fabrication shop. Essential safety equipment includes:
- Protective Helmets: To safeguard against falling objects.
- Goggles: Essential for protecting the eyes from sparks and debris during cutting and welding processes.
- Gloves: Heavy-duty gloves prevent cuts and abrasions when handling raw materials.
- Hearing Protection: Required in noisy environments to protect against long-term hearing damage.
Maintenance of Tools and Machinery
Regular maintenance of tools and machinery plays a crucial role in the efficiency and longevity of equipment in a steel fabrication shop. Key practices include:
- Routine Inspections: Conducting frequent checks on machinery to identify issues early.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Regularly cleaning machines and applying lubricants to ensure smooth operation.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: Timely replacement of blades, welding tips, and other components minimizes downtime and maintains performance.
Steel Fabrication Shop Workflow Optimization
Streamlining Operations
Efficient workflow is essential to maximizing productivity in a steel fabrication shop. Strategies for streamlining operations can include:
- Lean Manufacturing Techniques: Implementing principles that focus on waste reduction and optimizing processes.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establishing SOPs for processes enhances consistency and training for new employees.
- Task Prioritization: Effective scheduling of jobs based on urgency and complexity ensures that resources are allocated efficiently.
Efficient Inventory Management
Effective inventory management minimizes excess stock while ensuring necessary materials are available when required. Techniques include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Ordering materials as they are needed reduces storage costs and wastage.
- Inventory Tracking Software: Utilizing software systems for real-time tracking of inventory helps in better decision-making.
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic audits to reconcile physical inventory with system records aids in identifying discrepancies.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is vital to maintain high standards in fabrication processes. Implementation of various measures can include:
- Regular Inspections: Performing inspections at different fabrication stages ensures that defects are identified early.
- Testing Procedures: Utilizing destructive and non-destructive testing techniques to verify the integrity of welds and materials.
- Customer Feedback Loops: Analyzing feedback from clients helps in ongoing improvements and satisfaction adjustments.
Technology Integration in Steel Fabrication Shop
CAD Software for Fabrication Design
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has revolutionized how fabrication designs are created and modified. Key benefits include:
- Precision: CAD designs allow for high precision in measurements and reduces the scope of human error.
- Visualization: 3D modeling provides a clear view of the end product, facilitating better planning and modifications before physical work begins.
- Efficiency: Rapid revisions and enhancements can be made, significantly speeding up the design process.
Automation in Steel Fabrication
The integration of automation technology, such as robotic systems, increases efficiency and workspace safety:
- Robotic Welding: Automated welding systems enhance speed, consistency, and reduce human error.
- Automated Material Handling: Automated systems help in minimizing manual handling, reducing injury risks.
- Scheduling Automation: Software solutions can optimize job scheduling, ensuring resources are effectively utilized.
Data Analytics for Performance Monitoring
Utilizing data analytics in a steel fabrication shop offers insights into operational performance:
- Performance Metrics: Tracking productivity, downtime, and efficiency metrics aids in identifying areas for improvement.
- Forecasting: Data-driven forecasting can assist in material supply needs based on historical project data.
- Continuous Improvement: Insights derived from analytics can lead to iterative improvements in processes and technologies.
Future Trends in Steel Fabrication Shop
Sustainable Practices in Steel Fabrication
Sustainability has become a critical focus for many industries, including steel fabrication. Key practices include:
- Recycling Scrap Metal: Implementing processes to recycle scrap metal reduces waste and conserves resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Investing in energy-efficient machinery and practices can significantly lower the carbon footprint.
- Environmentally Friendly Materials: Researching and employing alternative materials that are less harmful to the environment.
Innovations in Materials Used
The evolution of materials affects fabrication methods. Innovations include:
- Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS): Increasing strength without increasing weight allows for lighter structures.
- Composite Materials: Employing composites in conjunction with steel for enhanced performance in specific applications.
- Smart Materials: Innovations that enable materials to change properties in response to external stimuli for specialized applications.
Industry 4.0 and Its Impact on Fabrication
The rise of Industry 4.0 signifies the next phase of digital transformation in manufacturing environments, including steel fabrication:
- IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) helps in real-time monitoring of machinery health, enhancing predictive maintenance strategies.
- Cloud Computing: Centralized data access and analytics can lead to better decision-making and coordinated operations across multiple sites.
- Collaborative Robots: As automation increases, robots that collaborate with human workers will enable more versatile and adaptive fabrication processes.